BIOMIMESYS® Adipose Tissue
3D cell culture model for adipose tissue
Product Basics
BIOMIMESYS® Adipose Tissue is a Hyaluronic acid (HA) based scaffold 3D cell culture model. This groundbreaking 3D cell culture technology associates the behavior of a solid scaffold and of a hydrogel, which we call “Hydroscaffold”. The Hydroscaffold’s composition and mechanical properties can mimics the microenvironment of adipose tissue. It is proven to provide better in vitro/in vivo correlation and cell longevity than 2D models.
Key Features
- Mimics the microenvironment of adipose tissue
- Better in vitro/in vivo correlation
- Better differentiation and cell longevity
- Ready to use
- Applicable for most downstream applications
- Batch to Batch consistent
Technical Information
Mimics the microenvironment of adipose tissue
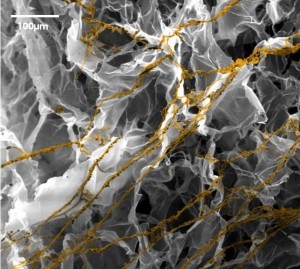
BIOMIMESYS® Adipose Tissue composition and organization are similar to in vivo adipose tissue by including collagens I, VI and fibronectin (RGDS pattern) in a cross-linked hyaluronic acid gel.
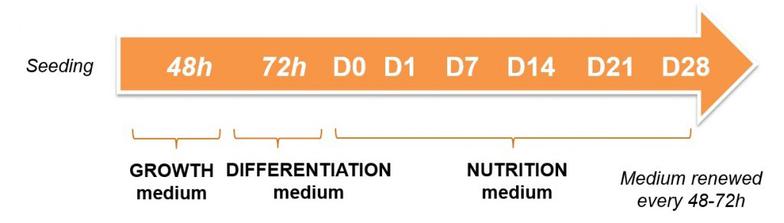
In order to demonstrate the induction of adipogenesis by the HCS Pharma hydroscaffold, BIOMIMESYS® Adipose tissue, various tests were performed on two cell types: 3T3-L1 and Human White Preadipocyte (HWP) according to the following culture protocol.
Protocol: as in 2D culture, seeding and differentiation steps are induced from day 0 (for HWP and 3T3-L1) until complete maturation.
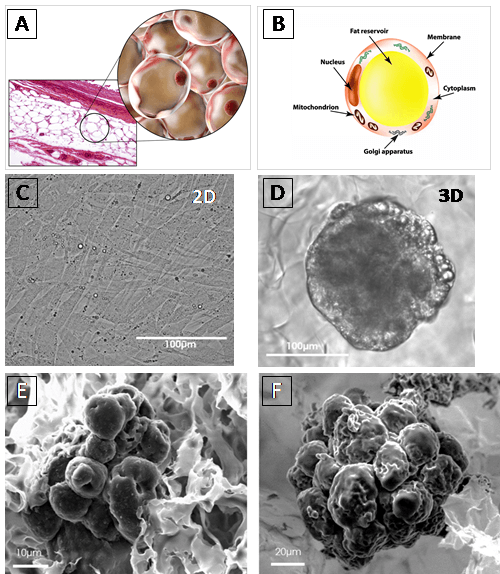
Figure: A and B: Adipocyte schematic morphology in vivo.
C and D: Light-microscopy images of adipocyte differentiated from preadipocyte HWP (Human white preadipocytes) at 7 days after seeded. HWP cultured in 2D exhibited a fibroblastic appearance (C), whereas in BIOMIMESYS® Adipocyte, it was resembling morphology of mature adipocytes in vivo, showing the establishment of their principal function, fat accumulation, resulting in the presence of vesicles (D).
E and F : SEM images of 3T3-L1 (murine preadipocytes) at day 7 (E) and HWP at day 14 (F), both were cultured in BIOMIMESYS® Adipocyte. In the hydroscaffold, adipocytes formed aggregates which increased in size over time.
Better differentiation and cell longevity
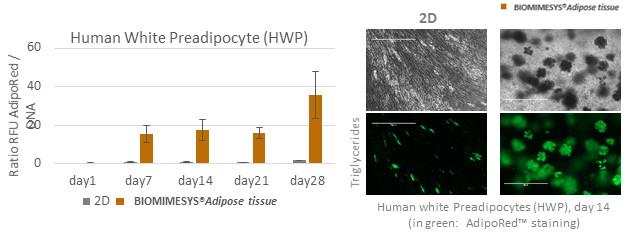
BIOMIMESYS® Adipose Tissue is dedicated to the culture of adipocytes: compared to 2D culture, primary human pre-adipocytes in BIOMIMESYS® Adipose Tissue (3D) showed optimal differentiation into adipocytes, and their functionality (such as lipid storage in a single large vacuole) was maintained until 28 days.
For a better in vitro/in vivo correlation
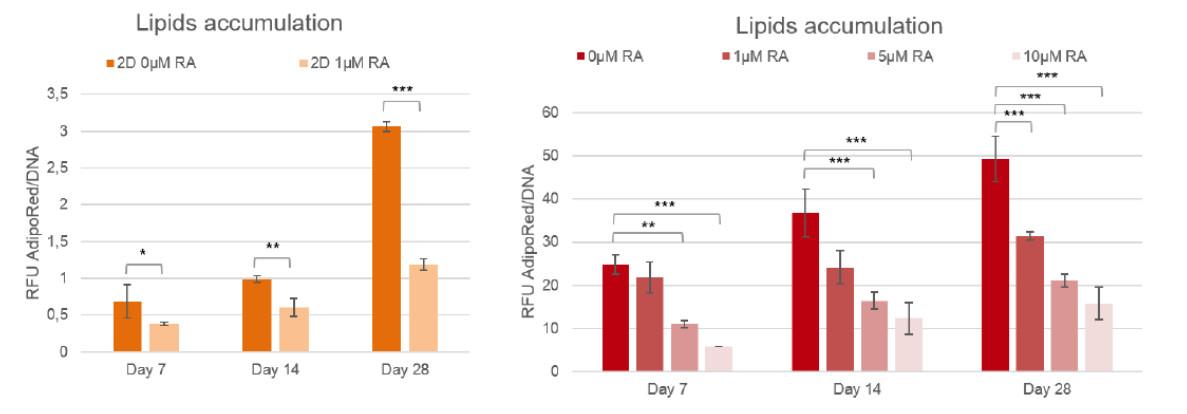
Figure 2: Lipid accumulation in 3T3-L1 with or with Retinoic acid, compared to 2D cultures (n=3, two-ways ANOVA statistics with Tukey post-hoc ; * : p<0,05 ; ** : p<0,01 ; *** : p<0,001)
To quantify the inhibition of lipogenesis, human pre-adipocytes and 3T3-L1 cells cultured in BIOMIMESYS® Adipose tissue and in 2D culture are treated with Retinoic acid, a well-known regulator. Lipid accumulation is measured using the AdipoRed ™ kit, normalized by DNA level.
As low as 1μM of Retinoic acid led to a significant lipids accumulation inhibition in 2D, whereas at least 5μM of this molecule was needed to significantly inhibit the lipogenesis of adipocytes grown in BIOMIMESYS® Adipose tissue.
Ready to Use
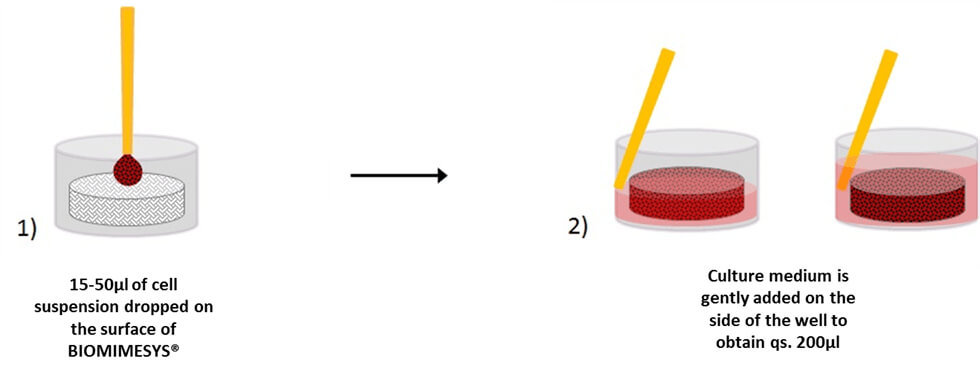
BIOMIMESYS® Adipose Tissue is EASY & READY TO USE. Upon receiving the vacuum sealed 96-well plate open it (under a hood) and add the cells directly on top of the matrix. Changing the culture medium is easy as well. To remove medium, simply draw the medium with a pipette between the matrix and the edge of the well. To refresh the medium, place fresh medium onto the surface of the matrix.
Successfully Tested Cells
Cell Lines
Human breast adenocarcinoma : MCF-7
Human breast carcinoma : CAL-51 / T-47D / MDAMB-231 / MCF10A
Normal mouse preadipocytes : 3T3-L1 / 3T3-F442A
Human colorectal adenocarcinoma : HCT 116
Normal human Keratinocytes : HaCaT
Normal human Fibroblasts : BJ
Primary Cells
Human white pre-adipocyte subcutaneous : HWP cryopreserved / HPrAD
Human Fibroblasts : NHDF
Human Keratinocytes : NHEK
Stem Cells
Human induced pluripotent stem cells : hiPS
Human sebocytes from induced pluripotent stem cells : PCi-SEB
Complete List of Tested Cells [PDF]
* Proof of Concept:
・In Vivo-like Morphology of Adipocytes [PDF]
・Increased Expression of Differentiation Genes [PDF]
・Higher Lipogenesis Activity [PDF]
・Maturation of Functional Human Adipocytes [PDF]
・Application: Regulation of Lipid Accumulation [PDF]
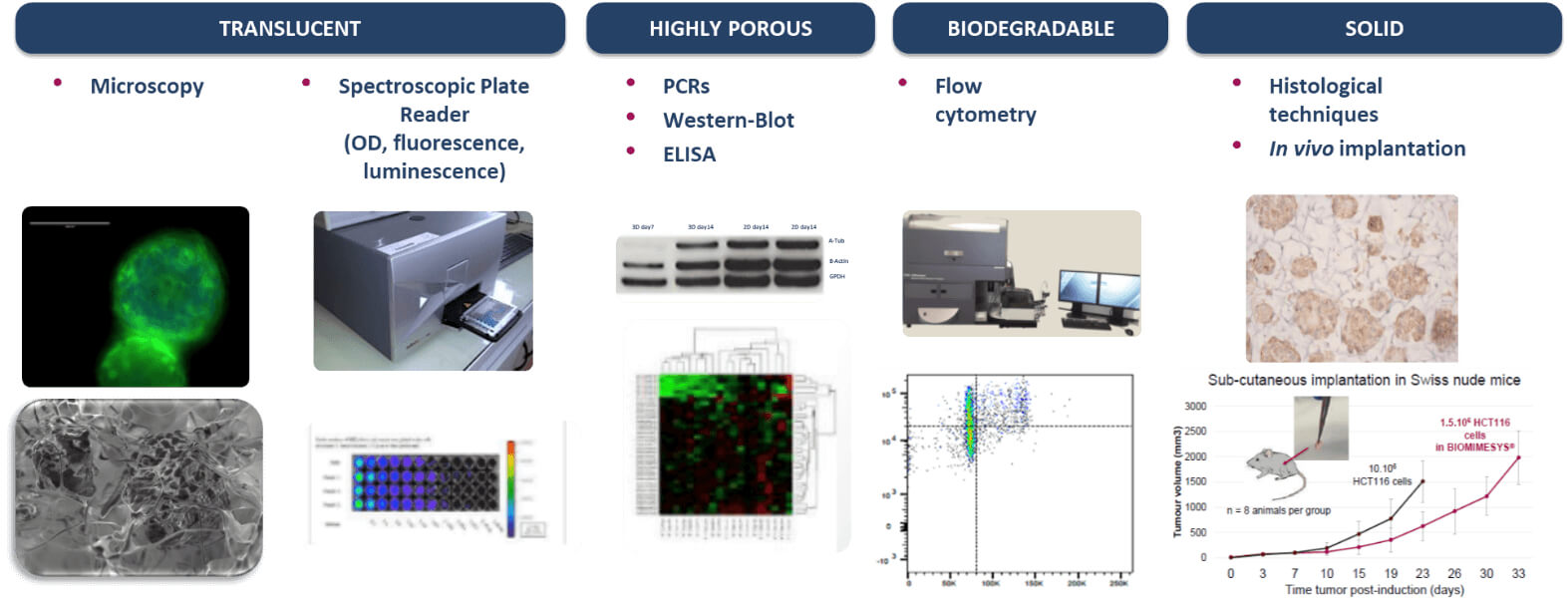
Compatible with Most Downstream Applications
BIOMIMESYS® hydroscaffold has many properties (transparent, porous, biodegradable, & solid) making it ideal for use with numerous downstream applications as shown below.
Specification
Composition:
- Hyaluronic acid (HA) (1.6MDa) grafted with RGDS
- Adipic acid dihydrazide (ADH) as crosslinker
- Collagen Type I & VI
Physicochemical Features:
- Young’s modulus: ~0.5kPa – different stiffness is available through customization
- Porosity: 120±50µm
Pricing

24 Hydrogel / 96 Well
Transparent Plate
- SKU: BIO_ADI_96_24_transp
- Price:
$410.00→ $369.00
Black Plate
- SKU: BIO_ADI_96_24_black
- Price:
$410.00→ $369.00
96 Hydrogel / 96 Well
Transparent Plate
- SKU: BIO_ADI_96_96_transp
- Price:
$590.00→ $531.00
Black Plate
- SKU: BIO_ADI_96_96_black
- Price:
$590.00→ $531.00
References & Literature
1. Louis, F. et al. A biomimetic hydrogel functionalized with adipose ECM components as a microenvironment for the 3D culture of human and murine adipocytes. Biotechnol Bioeng 114, 1813–1824 (2017) doi: 10.1002/bit.26306.
2. Neels, J. G., Thinnes, T. & Loskutoff, D. J. Angiogenesis in an in vivo model of adipose tissue development. FASEB J 18, 983–985 (2004) doi: 10.1096/fj.03-1101fje.
3. Cristancho, A. G. & Lazar, M. A. Forming functional fat: a growing understanding of adipocyte differentiation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 12, 722–734 (2011) doi: 10.1038/nrm3198.
4. Dalby, M. J., Gadegaard, N. & Oreffo, R. O. C. Harnessing nanotopography and integrin-matrix interactions to influence stem cell fate. Nat Mater 13, 558–569 (2014) doi: 10.1038/nmat3980.
5. McBeath, R., Pirone, D. M., Nelson, C. M., Bhadriraju, K. & Chen, C. S. Cell shape, cytoskeletal tension, and RhoA regulate stem cell lineage commitment. Dev Cell 6, 483–495 (2004) doi: 10.1016/S1534-5807(04)00075-9.
6. Wang, L., Johnson, J. A., Zhang, Q. & Beahm, E. K. Combining decellularized human adipose tissue extracellular matrix and adipose-derived stem cells for adipose tissue engineering. Acta Biomater 9, 8921–8931 (2013) doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2013.06.035.
Other Documents
- Retrieve Cells / Washing Gels
- First Steps - Co-culture, Change Medium, Seeding
- Protocol for Metabolic Activity Determination
- RNA or DNA Extraction
- Protein Extraction
- Microscopy
- Flow Cytometry
- Preparation of Samples for Histological Labeling
- Evaluation of BIOMIMESYS® hydroscaffold in mice bearing subcutaneous HCT 116 Human Colorectal tumour cells
- Technical Datasheet BIOMIMESYS® Adipose Tissue
- MSDS BIOMIMESYS® Adipose Tissue
FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY, NOT FOR USE IN DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES