ZenoParticle
A Polysaccharide Adjuvant
Product Basics
ZenoParticle CH-100 is a second-generation adjuvant developed using the proprietary technology of Zenogen Pharma. This micronized Chitosan (a polysaccharide) particle is biodegradable and easier to mix with antigens compared to oil-based adjuvants. It has been proven to cause less irritation at the injection site, thereby enabling multiple doses with less discomfort and pain for the host. It has also confirmed persistent antibody production using various methods/materials and immunostimulation when used with antigens in a research setting.
Key Features
- Micronized Chitosan (polysaccharide) particles developed by Zenogen Pharma's proprietary technology
- Made with biodegradable materials
- Proven to have low local irritation at the injection site
- Easier to mix with antigens compared to oil-based adjuvants
- Confirmed persistent antibody production with various methods and antigens
- Demonstrated immunostimulation
** This product is for research use only. Please do not use it on the humans**
**A License Agreement must be signed before purchasing this product. **
Technical Information
Persistent antibody production is induced in various administration routes
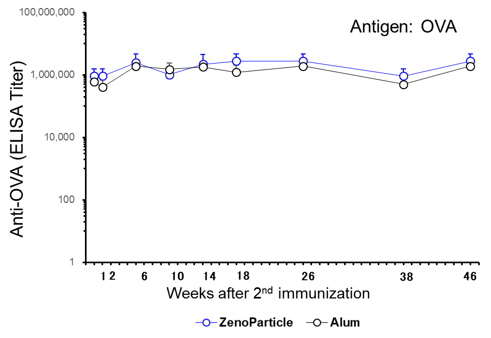
[Result 1]
Persistence of High Antibody Titer in Blood by Intraperitoneal Administration to Mice
1 μg of OVA, either with ZenoParticles or Alum, was administered intraperitoneally twice at 2-week intervals to 5-week-old female BALB/c mice (n=5). Blood was collected over time after the second immunization to measure the anti-OVA antibody titer by ELISA assay. An increase in antibody titer was observed one week after the second immunization, and similar levels were observed up to 46 weeks.
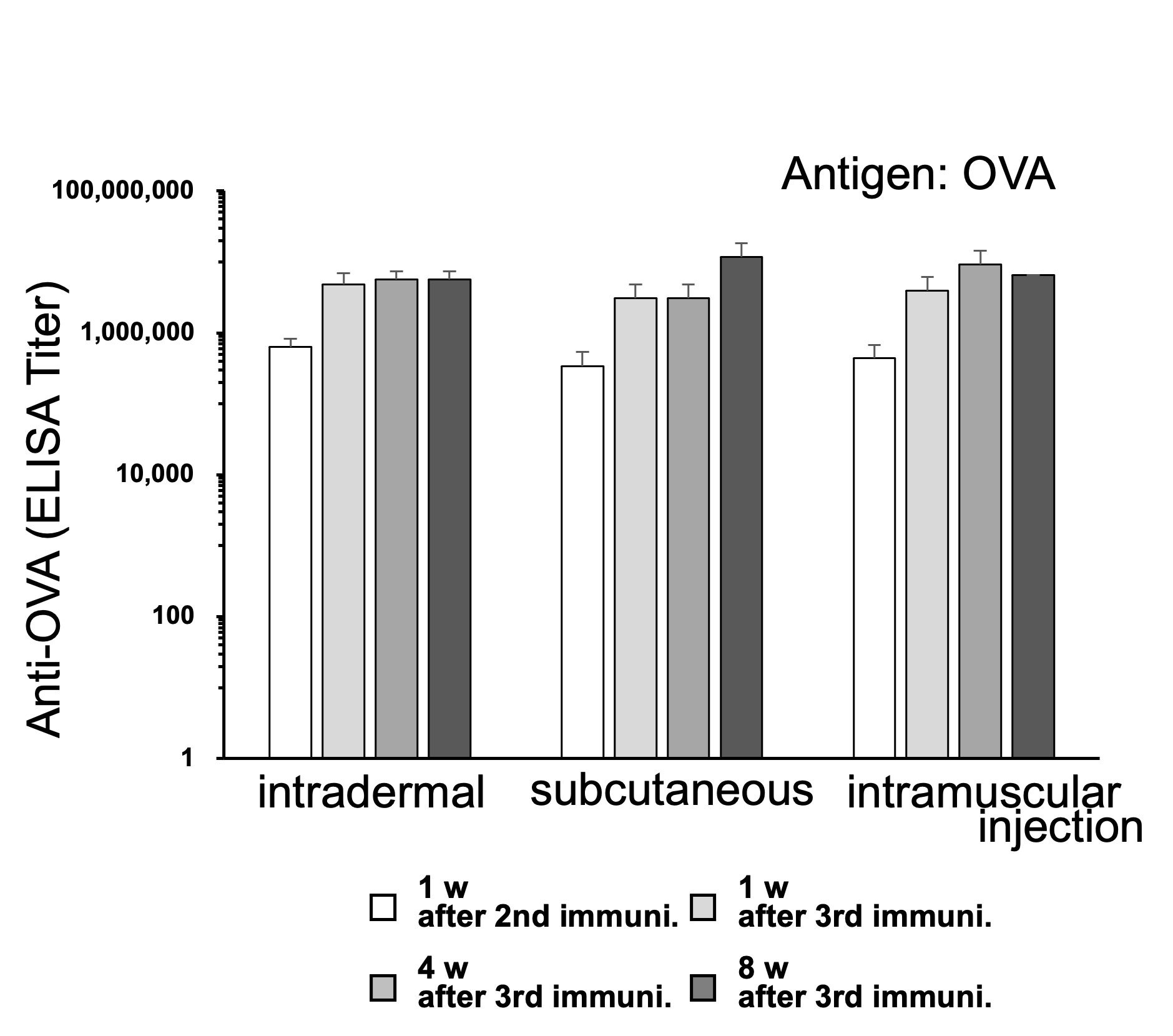
[Result 2]
Increased and Sustained Antibody Titers in Blood Following Intradermal, Subcutaneous, and Intramuscular Administrations
1 μg of OVA with ZenoParticles was administered intradermally, subcutaneously, or intramuscularly, three times at 2-week intervals to 5-week-old female BALB/c mice (n=5). Blood samples were collected one week after the second immunization and at one, four, and eight weeks after the third immunization. The anti-OVA antibody titer in blood was measured by ELISA. All intradermal, subcutaneous, and intramuscular administration routes showed an increase and persistence of the antibody titer, similar to intraperitoneal administration.
Immunostimulation is confirmed in tumor grafted mouse model
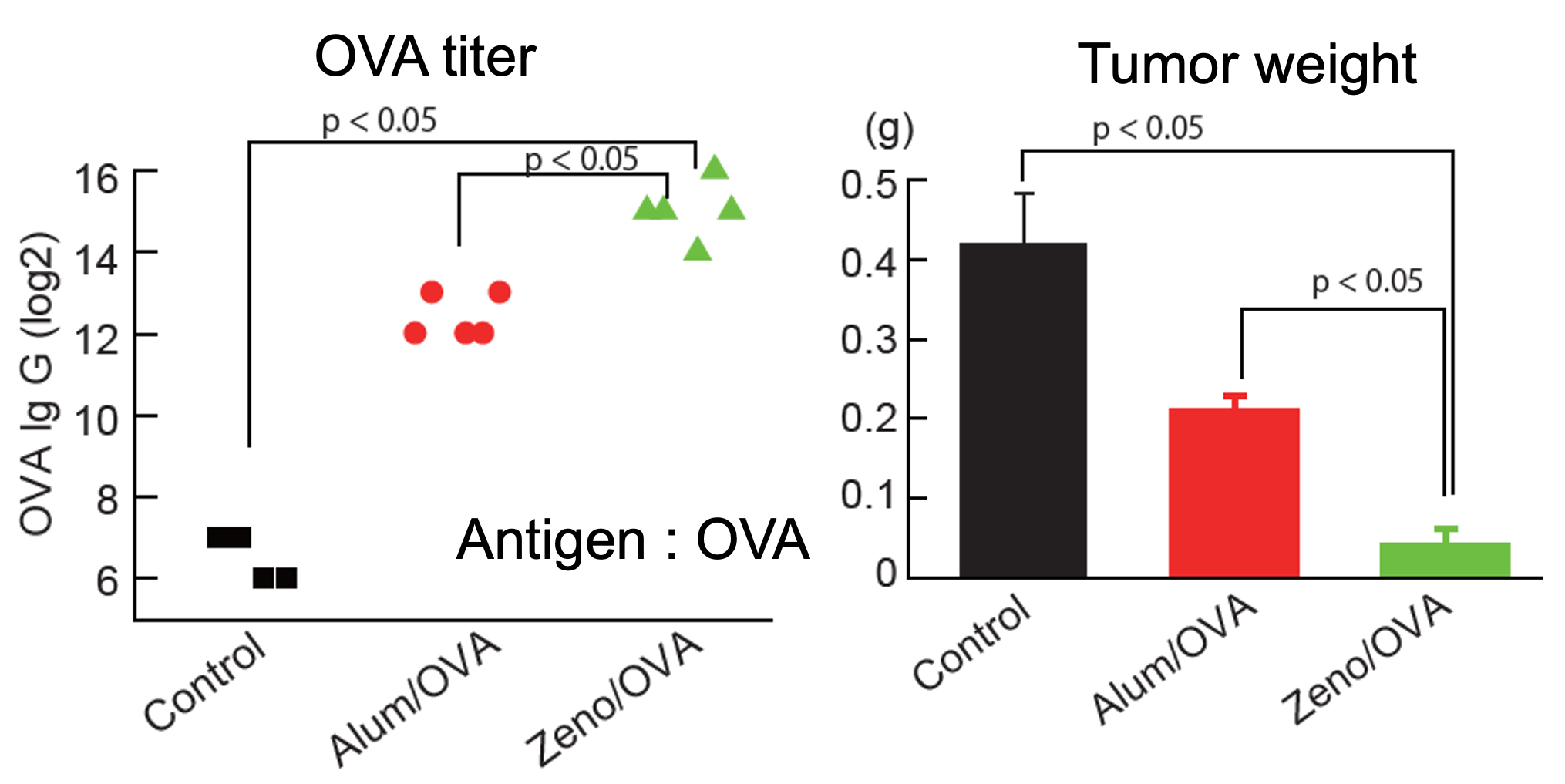
[Result 3]
Observation of Antigen-Specific IgG Production and Suppression of Tumor Growth in Tumor-Implanted Model Mice After Antigen Immunization
100μg of OVA, along with ZenoParticles or Alum, was administered subcutaneously to 8-week-old female C57BL/6 mice (n=5). Twelve days after the initial immunization, OVA-expressing B16F10 melanoma cells were subcutaneously implanted (2×105 cells/mouse). Two days after the implantation, a second immunization was administered.
28 days after the first immunization (fourteen days after the second immunization), the anti-OVA titer in blood and the tumor weight were measured. ZenoParticles showed a more significant effect with higher antigen-specific IgG production and better suppression of tumor growth than the Alum adjuvant.
(Research conducted at the joint research site)
Adjuvanticity confirmed when immunized with virus-derived proteins and peptide antigens.
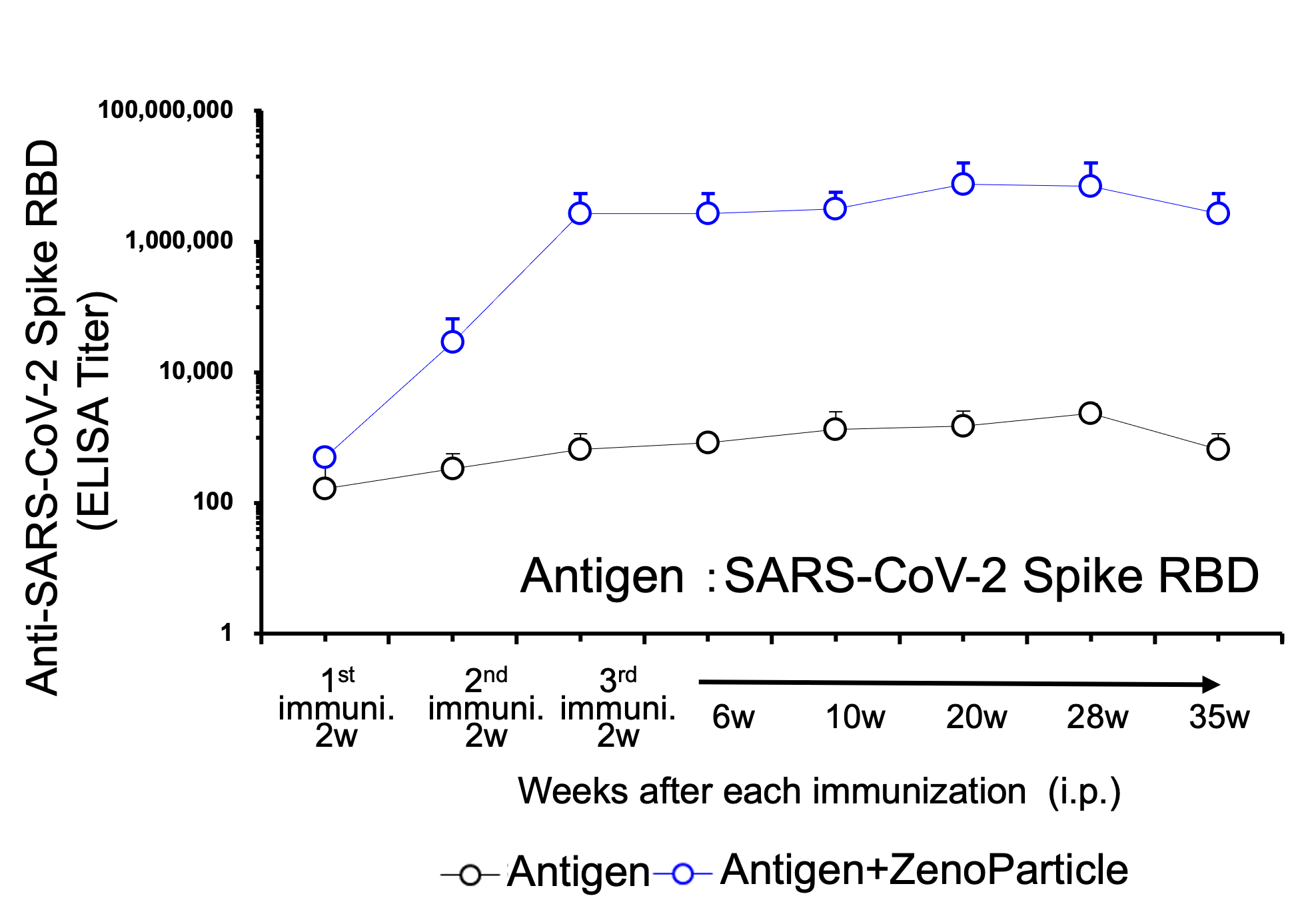
[Result 4]
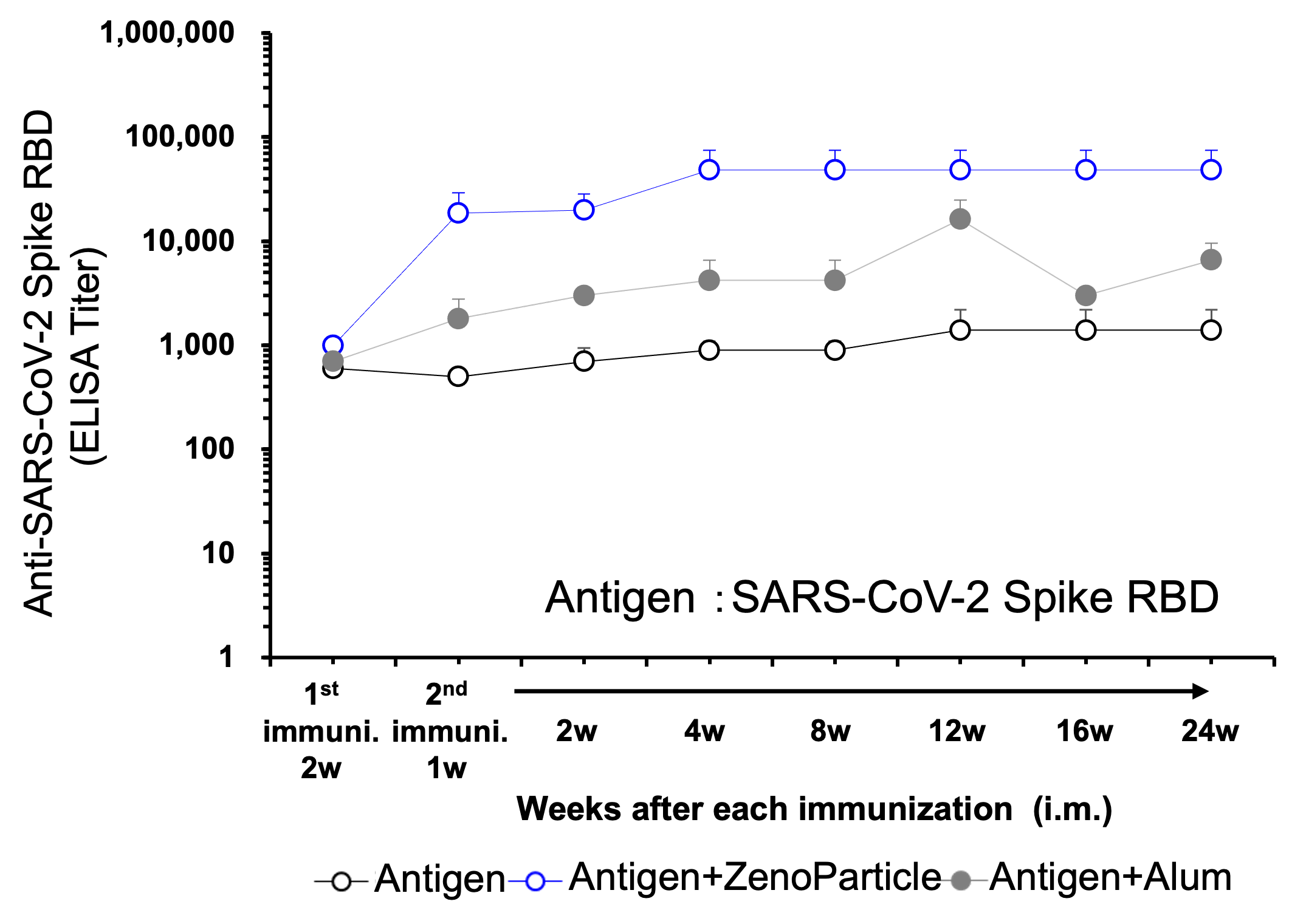
Maintained antibody titers in blood after immunized with viral protein antigen.
8-week-old female BALB/c mice (n=3) was immunized intraperitoneally with antigen protein (SARS-CoV-2 spike RBD) with ZenoParticles. The initial amount of antigen protein administered was 20μg. 2 weeks later 10μg was administered, then 2 weeks after that an additional 10ug was administered. Blood was collected and antibody titer was measured by ELISA assay, at 2 weeks after the first immunization, 2 weeks after the 2nd immunization, and 2, 6, 10, 20, 28, and 35 weeks after the 3rd immunization. Increase in antibody titer was observed from 2 weeks after the 2nd immunization, and the increased level was maintained from 2 weeks to 35 weeks after the 3rd immunization.
[Result 5]
Antibody titers elevated early and persisted long after immunization.
10μg of antigen protein (SARS-CoV-2 spike RBD) with ZenoParticles or Alum were administered 2 times at 2 weeks interval, intramuscularly to 5-week-old female BALB/c mice (n=5). The level of antibody titer in blood collected 2 weeks after the initial immunization was maintained for 24 weeks. ZenoParticle had higher titer than Alum.
[Result 5]
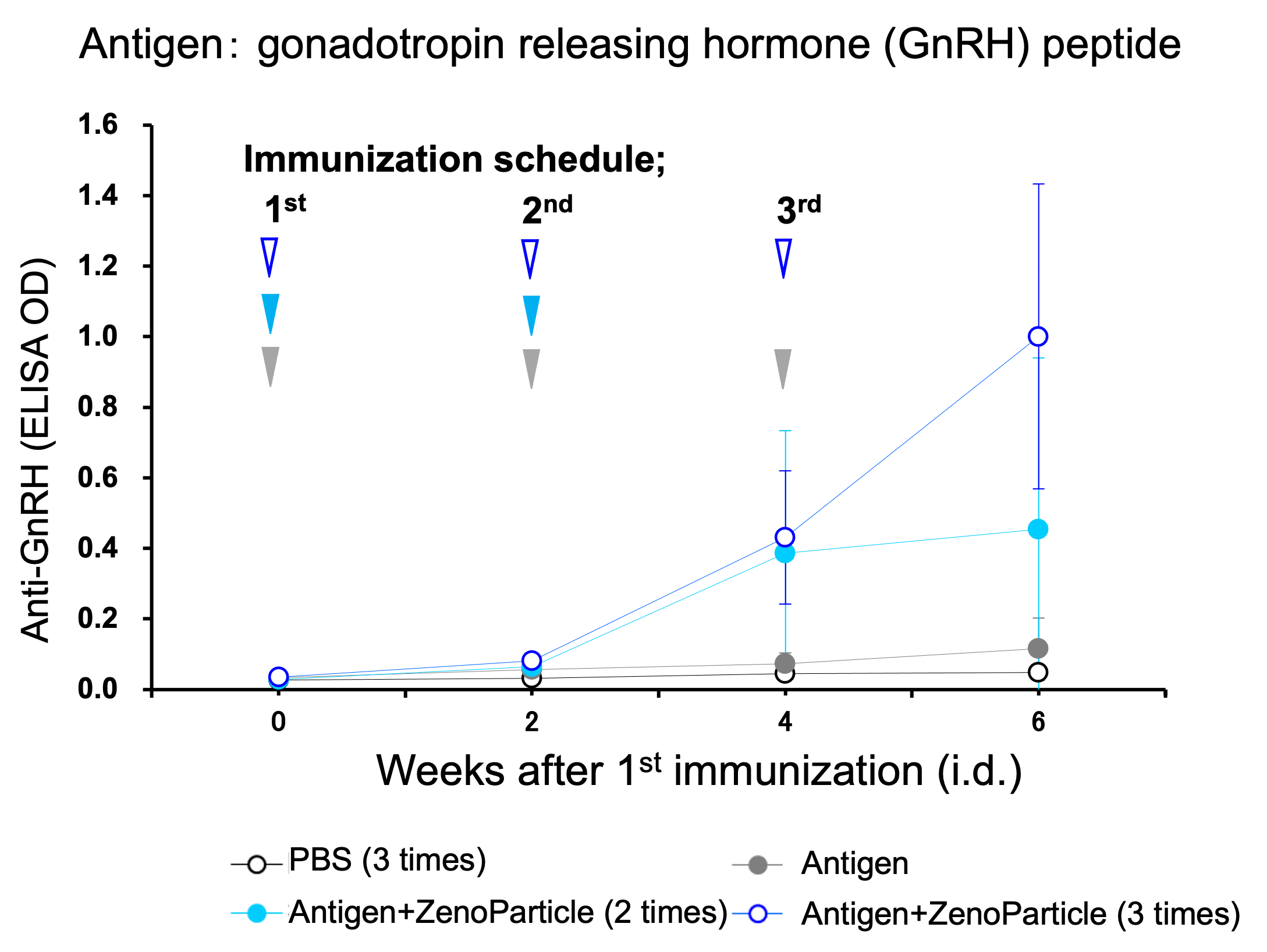
Blood antibody titers increased when a hormonal peptide antigen was immunized in rats.
9-weeks-old male Wistar Imamichi rats (n=4) were immunized by intradermal injection 3 times at 2 week intervals of 100µg antigen with or without ZenoParticle. Anti-GnRH antibody titer in blood after 1st immunization was periodically evaluated by ELISA..
An increase in antibody titer was observed 2 weeks after 2 immunizations, and the further increase in antibody titer was observed corresponding to the number of immunizations.
Protocol
- Prepare antigen solution and ZenoParicles.
- Prepare antigen solution using saline or other similar solution. The needed volume of the solution equals to that of ZenoParticles to be used.
- Adjust the antigen concentration of the solution based on characteristics of the antigen. Precipitation may occur if the antigen concentration is too high or due to the nature of the antigen.
- Bring a tube of ZenoParticle from refrigeration to room temperature and stir. (Using a vortex mixer recommended). At room temperature it may appear cloudy, but that is not a problem for use.
- Mix the prepared antigen solution and ZenoParticle in a 1:1 ratio.
- Stir the mixture at room temperature. (Using a vortex mixer recommended)
- Use the mixture immediately after confirming that the antigen solution and ZenoParticle are sufficiently mixed.
- 100 to 200μL of injection per mouse is suitable for intraperitoneal administration.
Specification
- Size: 500mL x5 package
- Storage temperature: 2-8°C
- Manufactured by: Zenogen Pharma Co., Ltd.
Pricing
References
- Wen, Z.-S.-X., Ying-LeiAU-Zou, Xiao-TingAU-Xu, Zi-RongTI-Chitosan Nanoparticles Act as an Adjuvant to Promote both Th1 and Th2 Immune Responses Induced by Ovalbumin in Mice. Chitosan Nanoparticles Act as an Adjuvant to Promote both Th1 and Th2 Immune Responses Induced by Ovalbumin in Mice. Marine Drugs 9, 1038–1055 (2011) doi: 10.3390/md9061038.
- Carroll, Elizabeth. C. et al. The Vaccine Adjuvant Chitosan Promotes Cellular Immunity via DNA Sensor cGAS-STING-Dependent Induction of Type I Interferons. Immunity 44, 597–608 (2016) doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.02.004.
- Li, H., Willingham, S. B., Ting, J. P.-Y. & Re, F. Cutting Edge: Inflammasome Activation by Alum and Alum’s Adjuvant Effect Are Mediated by NLRP3. J. Immunol. 181, 17 (2008) doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.1.17.
- Pifferi, C., Fuentes, R. & Fernández-Tejada, A. Natural and synthetic carbohydrate-based vaccine adjuvants and their mechanisms of action. Nature Reviews Chemistry 5, 197–216 (2021) doi: 10.1038/s41570-020-00244-3.
- Alu, A. et al. Intranasal COVID-19 vaccines: From bench to bed. eBioMedicine 76, (2022) doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.103841.
Other Documents
- Protocol - Coming soon
- SDS - Coming soon
- Sample CoA
Related Products
There are related products.
FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY, NOT FOR USE IN DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES